What is glaucoma?
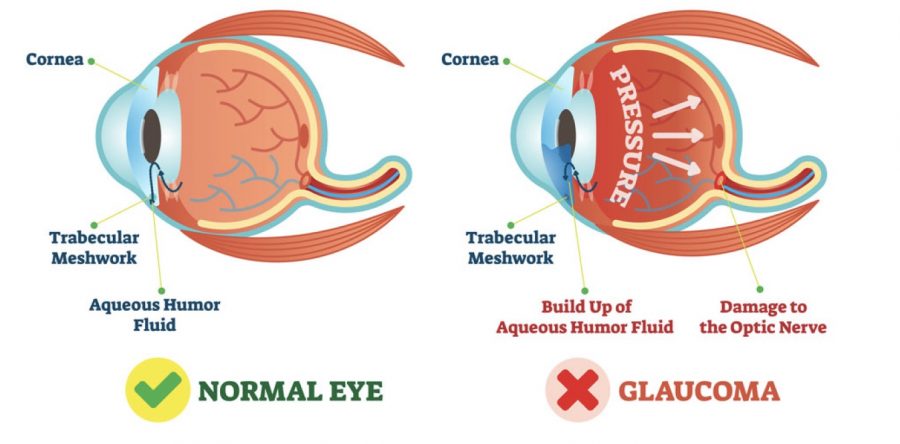
Glaucoma is the second leading cause of blindness. It is a group of diseases that damages the optic nerve, the connection of the eye to the brain, and may lead to progressive, irreversible vision loss. The main cells affected by glaucoma are the retinal ganglion cells and these cells process visual information from light entering into the eye and transmit it to the brain by axons, which make up the optic nerve. These cells allow you to send images to the brain and do not regenerate if damaged.
Glaucoma is usually related to high intraocular pressure. It can also be caused by certain conditions to the eye such as inflammation,severe cataracts and trauma which can affect the drainage of the fluid in the eye causing it to become closed or narrow. This pressure pushes on the optic nerve thus damaging the cells. However, glaucoma can be found in patients who have low intraocular pressure as well.
Early signs of glaucoma
The only way to detect early signs of glaucoma is through a comprehensive eye examination. Glaucoma does not show symptoms until laters stages. Thus, it is significant to get your eyes examined despite having good vision, especially if there is family history of glaucoma. Early detection can help slow the progression of the disease.
Symptoms that you may notice if glaucoma goes undiagnosed:
- Loss of peripheral vision
- Difficulty adjusting to dark rooms
- Blurry vision especially in the morning
- Halos around light
- Pain
- Headache
Keep in mind, different types of glaucoma do have different symptoms depending on the root cause.
Diagnosing glaucoma
In order to diagnose glaucoma, there are a variety of tests performed. Patients who are glaucoma suspects will be followed carefully and testing will be performed and used to compare to the baseline information.
Tests
Optical Coherence Tomography
An imaging machine used to scan the back of the eye (retina and optic nerve). This will provide us with measurements that will help with the diagnosis and management of many conditions such as glaucoma.
Visual Field
A special computerized test done to assess central and peripheral vision, as well as detect certain neurological defects. This test can provide early diagnosis for many eye diseases long before they become clinically detectable.
Fundus photography
Offers a high-quality digital photography of your optic nerve for those patients who want to record the appearance of this vital structure today before disease occurs.
Gonioscopy
An examination to look at the front part of your eye (anterior chamber) between the cornea and the iris. It is painless and examines whether the area where fluid drains out of your eyes (called the drainage angle) is open or closed.
Pachymetry
A medical device used to measure the thickness of the eye’s cornea.
Treatment
The treatment for glaucoma focuses on lowering the eye pressure in the eyes. Prescription eyes drops and oral medications are the most common course of treatment. If they are not effective, laser surgery may be considered. In severe cases, a shunt may be placed in the eye to assist in draining excess fluid for managing the pressure.
If you have any questions, please feel free to contact us and/or schedule an appointment!
Author: Dr. Ia Ong Her


